NgRx Router Store | Reduce & Select Route Params
Posted by Simar Paul Singh on 2019-01-22
NgRx is an implementation of Flux Pattern for angular leveraging RxJs. Inspired by Redux it uses a centralized state store approach.
What’s the genius behind?
State is centralized and all mutations are requested by dispatching discrete actions. Reducers are pure functions (action, current-state ) => (new-state) which apply action to the current-state to produce new-state (new instance) with changes applied.
Centralizing your application’s state and logic enables powerful capabilities like undo/redo, state persistence, and much more.
We can watch changes, react with side-effects, use “time-travel debugging”, and send complete error reports to a server.
Redux DevTools make it easy to trace when, where, why, and how application’s state changed.
Most of the advantages of using this kind of architecture stem from use of centralized state store. In good a NgRx implementation Container components must depend only on the Store for state (selectors and actions).
Router is an essential part of an App’s state
If an application uses routes / navigation, the routing becomes an essential part of your application state.
Without incorporating Router in your Store, container components can’t depend on store alone. Components then also need Router / ActivatedRouteSnapshot to figure out path / query params needed to select state of slice from Store and / or dispatch actions to modify the state slice with respect to the current route.
What happens router state isn’t part of your central store?
Code Duplication
Letting
componentsto extractpath/queryparams from navigation / router-state and then use it to select respective state slices and / or dispatch actions we end up with lot of code duplication between sibling components and unnecessary coupling between parent and children components where a child component may need a router param extracted by parent component along side its own.
Inconsistency
Users may navigate to a nested route directly, for example by clicking on a shared link, bookmark or even typing in route in browsers navigation bar. We need route params to establish / select the state for target component trees mounted in one ore more the
<route-outlets/>before anything meaningful can render.
Unmaintainable
We can’t replay or jump across state snapshots using the redux dev tools as route changes if weren’t reduced by NgRx, can’t be jumped-to or re-played.
/* src/app/pages/ticket-detail/ticket-detail.component.ts */
import {Component, ElementRef, OnInit, ViewChild} from '@angular/core';
import {ActivatedRoute, Router} from '@angular/router';
import {concat, Observable, of} from 'rxjs';
import {catchError, map, switchMap, tap, combineLatest} from 'rxjs/operators';
import {BackendService, Ticket} from '../../services/backend.service';
import {select, Store} **from** '@ngrx/store';
import {getTickets} **from** '../../reducers/ticket';
@Component({
selector: 'app-ticket-detail',
templateUrl: './ticket-detail.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./ticket-detail.component.css']
})
export class TicketDetailComponent implements OnInit {
ticket$: Observable<Ticket>;
tickets$: Observable<Ticket[]>;
constructor(
private activatedRoute: ActivatedRoute,
private store: Store,
private router: Router) {
...
this.tickets$ = this.store.pipe(select(getTickets));
this.ticket$ =
activatedRoute.params.pipe(
map(p => p.id),
combineWithLatest(tickets$),
switchMap(([id, tickets]) => tickets[id],
catchError(error => of({error})),
tap(value => this.form.patchValue({...value}))
);
}
...
}
Solution
Following the principle of dependency inversion, if Components extract path / query params from Router state just to use them with their interactions with Store, why not let store/selectors and reducers/side-effects deal with the router and let components depend only the Store?
We need ngrx-router-storeto reduce route changes into the store and dispatch route change events on the actions stream to allow routes and their mutation to be the part of centralized state in the store.
Let us wire ngrx-router-store to the App’s NgRx store
npm install @ngrx/router-store — save
If like me, you find angular’s router API hard to collect all path params in the route. Wouldn’t it be nice if we could get all routing state data {data, params, queryParams} ?
/* ./src/app/reducers/router/merged-route.ts */
import {Data, Params} from '@angular/router';
export interface MergedRoute {
url: string;
queryParams: Params;
params: Params;
data: Data;
}
We can recourse to ngrx-router-store with custom RouterStateSerializer<T> to give us routing state in a form we like <T= MergedRoute>
/* src/app/reducers/router/merged-route-serialzer.ts */
import {RouterStateSerializer} from '@ngrx/router-store';
import {ActivatedRouteSnapshot, Data, Params, RouterStateSnapshot} from '@angular/router';
import {MergedRoute} from './merged-route';
export class MergedRouterStateSerializer implements RouterStateSerializer<MergedRoute> {
serialize(routerState: RouterStateSnapshot): MergedRoute {
return {
url: routerState.url,
params: mergeRouteParams(routerState.root, r => r.params),
queryParams: mergeRouteParams(routerState.root, r => r.queryParams),
data: mergeRouteData(routerState.root)
};
}
}
function mergeRouteParams(route: ActivatedRouteSnapshot, getter: (r: ActivatedRouteSnapshot) => Params): Params {
if (!route) {
return {};
}
const currentParams = getter(route);
const primaryChild = route.children.find(c => c.outlet === 'primary') || route.firstChild;
return {...currentParams, ...mergeRouteParams(primaryChild, getter)};
}
function mergeRouteData(route: ActivatedRouteSnapshot): Data {
if (!route) {
return {};
}
const currentData = route.data;
const primaryChild = route.children.find(c => c.outlet === 'primary') || route.firstChild;
return {...currentData, ...mergeRouteData(primaryChild)};
}
To make router state {params, queryParams, data}: MergedRoute a part of our centralized NgRx store state['router'], we will write a module that can simply be included in your App’s root module
/* ./src/app/router/ngrx-router.module.ts */
import {NgModule, Optional, Self} from '@angular/core';
import {routerReducer, RouterStateSerializer, StoreRouterConfig, StoreRouterConnectingModule} from '@ngrx/router-store';
import {StoreModule} from '@ngrx/store';
import {MergedRouterStateSerializer} from './merged-route-serialzer';
import {Router} from '@angular/router';
export const routerStateConfig = {
stateKey: 'router', // state-slice name for routing state
};
@NgModule({
imports: [
StoreModule.forFeature(routerStateConfig.stateKey, routerReducer),
StoreRouterConnectingModule.forRoot(routerStateConfig),
],
exports: [
StoreModule,
StoreRouterConnectingModule
],
providers: [
{
provide: RouterStateSerializer,
useClass: MergedRouterStateSerializer,
}
]
})
export class NgrxRouterStoreModule {
constructor(@Self() @Optional() router: Router) {
if (router) {
console.log('All good, NgrxRouterStoreModule');
} else {
console.error('NgrxRouterStoreModule must be imported in the same same level as RouterModule');
}
}
}
Let us include the module we defined above into our App’s root module.
import {ActionReducerMap, MetaReducer, StoreModule} from '@ngrx/store';
import {storeFreeze} from 'ngrx-store-freeze';
import {NgModule} from '@angular/core';
import {StoreDevtoolsModule} from '@ngrx/store-devtools';
import {environment} from '../../environments/environment';
import {routes} from './routes';
import {EffectsModule} from '@ngrx/effects';
import {effects} from './effects';
import {NgrxRouterStoreModule} from './router/ngrx-router.module.ts';
export const metaReducers: MetaReducer<{}>[] =
!environment.production ? [storeFreeze] : [];
@NgModule({
imports: [
StoreModule.forRoot(reducers as ActionReducerMap<{}>, { metaReducers }),
EffectsModule.forRoot(effects),
!environment.production ? StoreDevtoolsModule.instrument() : [],
NgrxRouterStoreModule,
BrowserModule,
RouterModule.forRoot(routes:)
]
})
export class AppModule {
}
Router should then be hooked in to your NgRx store. Open redux-dev-tools to see ROUTER_NAVIGATION events with routing state.
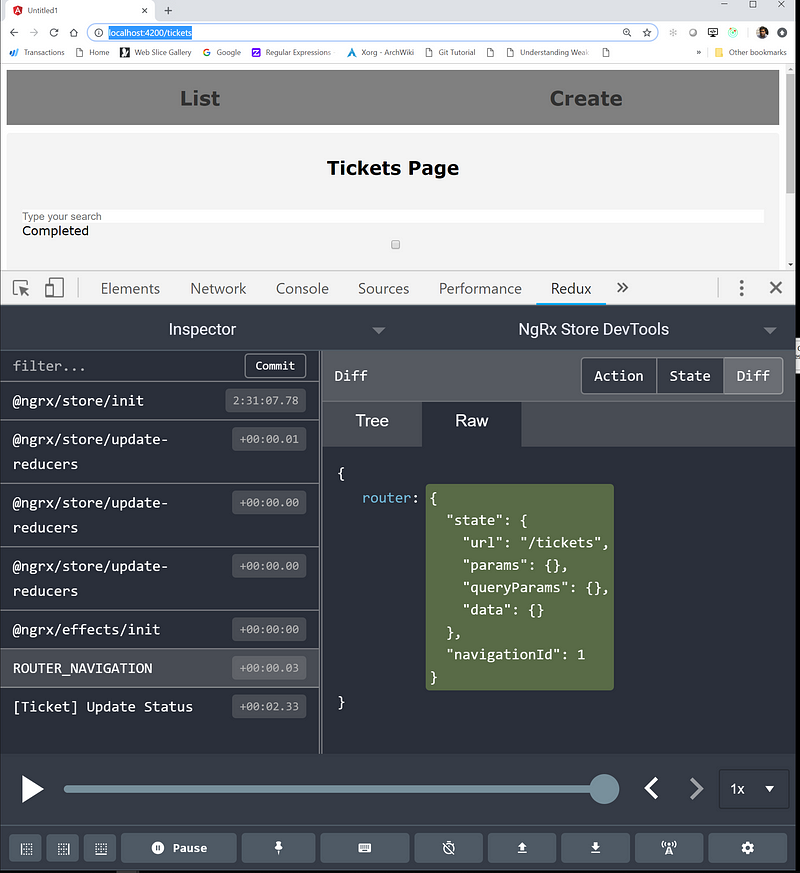
Next we will write selectors for state.router : MergedRoute so we can access to project routing information in any selector and components can be freed from extracting params / queryParams.
/* src/app/reducers/router/router-state.selectors.ts */
import {createFeatureSelector, createSelector} from '@ngrx/store';
import {routerStateConfig} from './ngrx-router.module';
import {MergedRouteReducerState} from './index';
export const getRouterReducerState = createFeatureSelector<MergedRouteReducerState>(routerStateConfig.stateKey);
export const getMergedRoute = createSelector(getRouterReducerState, (routerReducerState) => routerReducerState.state);
For example, if we have component that renders detail of an entity, Ticket based on the :ticketId path param in the route
/* src/app/reducers/ticket/ticket.selector.ts */
import {createFeatureSelector, createSelector} from '@ngrx/store';
import {TicketReducerState} from './ticket.reducers';
import {ticketStateConfig} from './ticket.state';
import {getMergedRoute} from '../router/router-state.selectors.ts'
export const getTicketReducerState = createFeatureSelector<TicketReducerState>(ticketStateConfig.stateKey);
export const getTickets = createSelector(getTicketReducerState, (ticketReducerState) => ticketReducerState.state);
export const getSelectedTicket = createSelector(getTickets, getMergedRoute,(tickets, mergedRoute) => mergedRoute.params.ticketId);
Finally, here how we can re-write our ticket-detail component to only depend on centralized store
/* src/app/pages/ticket-detail/ticket-detail.component.ts */
import {Component, ElementRef, OnInit, ViewChild} from '@angular/core';
import {ActivatedRoute, Router} from '@angular/router';
import {concat, Observable, of} from 'rxjs';
import {catchError} from 'rxjs/operators';
import {BackendService, Ticket} from '../../services/backend.service';
import {select, Store} from '@ngrx/store';
import {getSelectedTicket} from '../../reducers/ticket';
@Component({
selector: 'app-ticket-detail',
templateUrl: './ticket-detail.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./ticket-detail.component.css']
})
export class TicketDetailComponent implements OnInit {
ticket$: Observable<Ticket>;
constructor(private store: Store) {
...
this.ticket$ = this.store.pipe(select(getSelectedTicket));
}
...
}
Notice we don’t need to deal with Router, ActivatedRouteSnapshot and battery of RxJs operations to ActivatedRouteSnapshot with store selector getTickets.
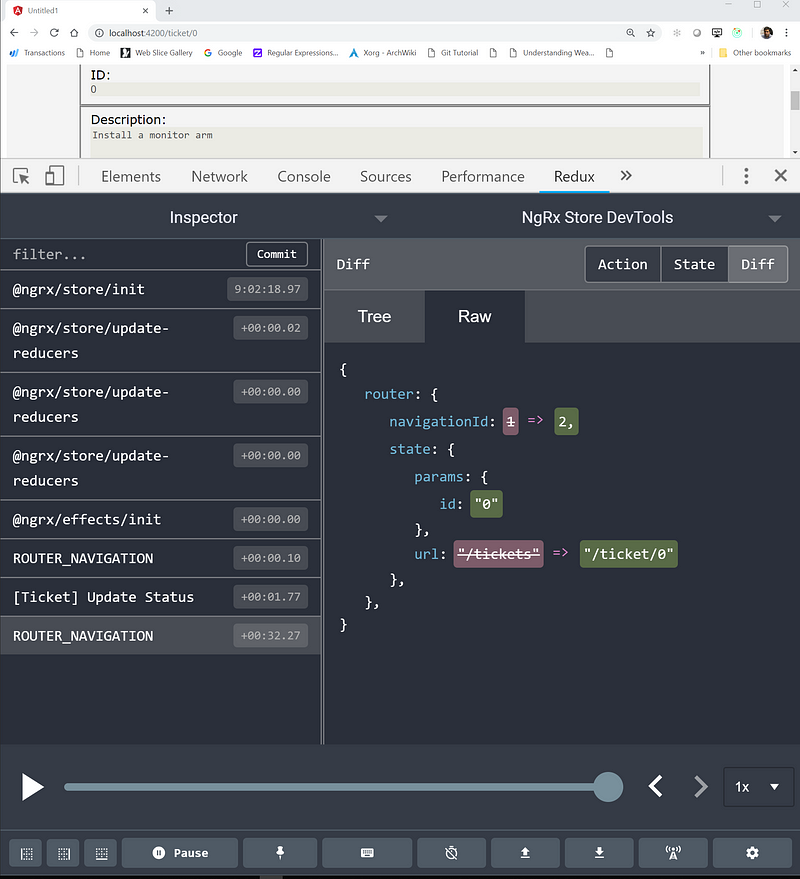
Also, now in your redux-dev-tool, you can work debug easily, replay, jump to any state snapshot, routing actions will be played along.
This article is also aviable on my Medium publication. If you like the artile, or have any comments and suggestions, please clap or leave comments on Medium.